Getting started with OpenShift Service Mesh
This tutorial explains how to use the OpenShift Service Mesh to manage the bookinfo demo application.
Requirements
To follow this guide, please make sure that you have the following tools installed:
oc-
You can download the OpenShift command directly from OpenShift Web Console. Open the help menu (marked as a question mark at the top right) and select the "Command line tools" entry.
Step 1: Creating the ServiceMeshControlPlane
The ServiceMeshControlPlane manages all services that are part of a service mesh. Creating multiple control planes allows for creating multiple independent service meshes, for example in a multi-tenancy environment.
-
Create a new namespace called
demo-ossm-controlplaneoc new-project demo-ossm-controlplaneIf you get an error that the namespace already exists, please pick another name and try again. We recommend prefixing the name with the name of your organization to minimize potential for name collisions.
-
Create a ServiceMeshControlPlane
oc create -n demo-ossm-controlplane -f - <<EOF apiVersion: maistra.io/v2 kind: ServiceMeshControlPlane metadata: name: basic spec: version: v2.3 tracing: type: Jaeger sampling: 10000 addons: jaeger: name: jaeger install: storage: type: Memory kiali: enabled: true name: kiali grafana: enabled: true EOF -
Watch the progress of the control plane deployment
oc get pods -n demo-ossm-controlplane -w -
Verify the control plane is ready
oc get smcp -n demo-ossm-controlplaneYou should see your new ServiceMeshControlPlane with status
ComponentsReady.
Step 2: Creating the Service Mesh member roll
The ServiceMeshMemberRoll associates OpenShift projects with ServiceMeshControlPlanes. Each project can belong to only one Control Plane, but one Control Plane can manage multiple projects. The ServiceMeshControlPlane can only manage services in projects that are associated with it via a ServiceMeshMemberRoll.
-
Create a new project to contain the application that shall be part of the service mesh
oc new-project demo-ossm-bookinfo -
Create a ServiceMeshMemberRoll in the control plane namespace to associate this new project with the control plane
oc create -n demo-ossm-controlplane -f - <<EOF apiVersion: maistra.io/v1 kind: ServiceMeshMemberRoll metadata: name: default spec: members: - demo-ossm-bookinfo EOF -
Verify the ServiceMeshMemberRoll was successfully created
oc get smmr -n demo-ossm-controlplane defaultA status of
Configuredindicates that installation was successful.
Step 3: Deploying the bookinfo demo application
bookinfo is a small sample application which is built from microservices.
It displays information about a book.
The main productpage service calls other microservices to collect information and reviews pertaining to a book.
-
Deploy the Bookinfo application from its manifest:
oc apply -n demo-ossm-bookinfo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Maistra/istio/maistra-2.3/samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml -
Deploy the ingress gateway, which allows public access to the application
oc apply -n demo-ossm-bookinfo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Maistra/istio/maistra-2.3/samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml -
Deploy the destination rules for the application, which configure the routing between the individual microservices
oc apply -n demo-ossm-bookinfo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Maistra/istio/maistra-2.3/samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all.yaml -
Verify all pods are ready
oc get pods -n demo-ossm-bookinfo
Step 4: Enable sidecar injection
To avoid interference between different operators, the OpenShift Service Mesh controller refuses to touch any deployments that aren’t annotated a certain way. We need to add this annotation to all our deployments to allow the controller to inject the necessary sidecars.
-
Check all the deployments of our application
oc get deployment -n demo-ossm-bookinfo -
Add the annotation to all deployments
oc get deployment -n demo-ossm-bookinfo -o NAME | while read line ; do oc annotate "$line" -n demo-ossm-bookinfo "sidecar.istio.io/inject=true" ; doneThe bookinfo application technically already has sidecar injection enabled by default. However, the step is highlighted here anyways, since it’s necessary on any custom workloads.
-
View the bookinfo application in your browser
Run the following to get the application URL:
export GATEWAY_URL=$(oc -n demo-ossm-controlplane get route istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}') echo "http://$GATEWAY_URL/productpage" -
You can use the following command to generate some traffic to your application for testing:
while true ; do curl "http://$GATEWAY_URL/productpage" > /dev/null ; sleep 1 ; done
Step 5: Explore your microservices using the tools provided by OpenShift Service Mesh
-
Navigate to kiali
-
Find the URL using this command:
oc -n demo-ossm-controlplane get route kiali -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}' -
Click on "Log In with OpenShift" to log into Kiali
-
Navigate to
Graphto see an overview of your service mesh.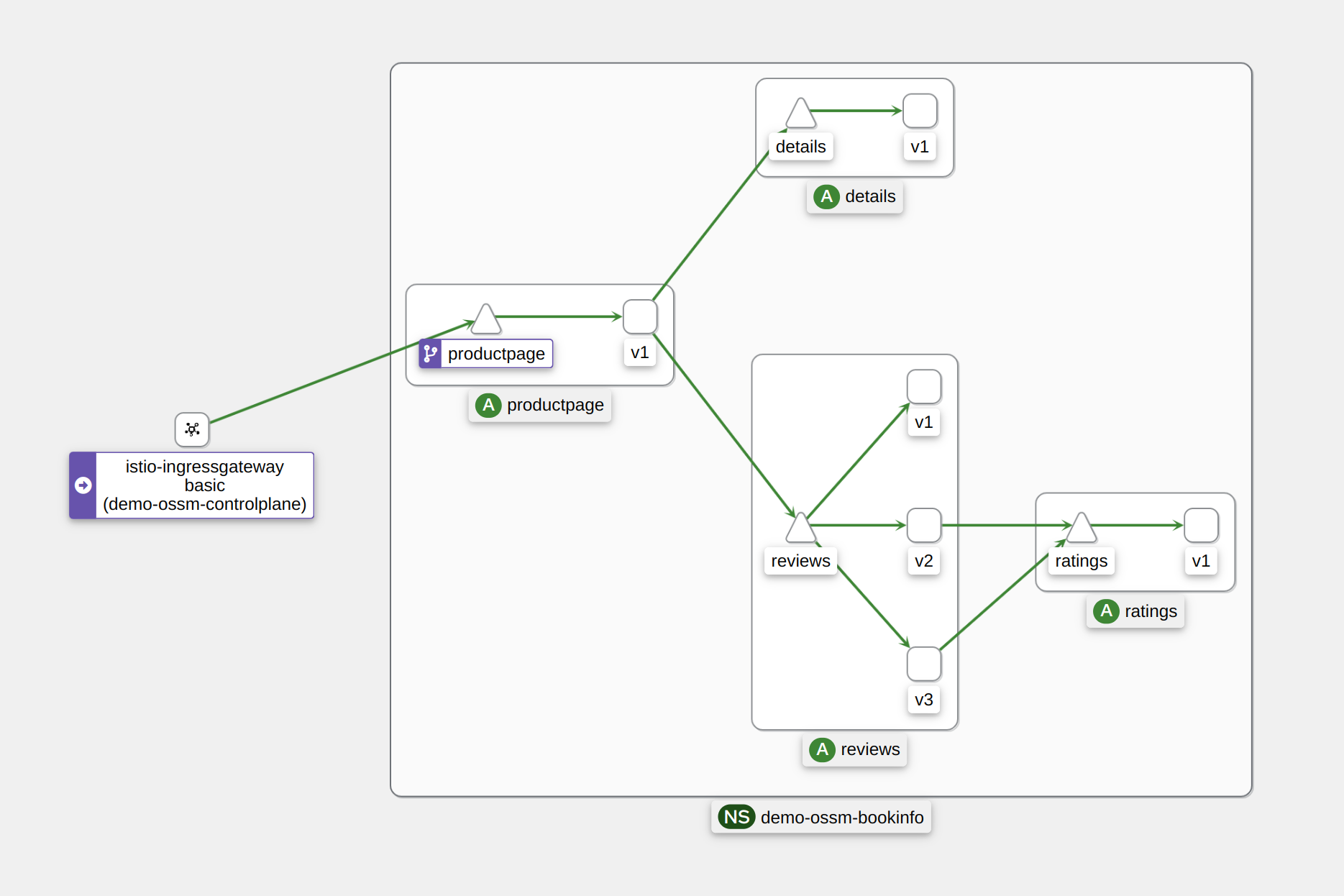
-
For more information on Kiali and its features, see the Kiali documentation.
-
-
Navigate to Jaeger
-
Find the URL using this command:
oc -n demo-ossm-controlplane get route jaeger -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}' -
Click on "Log In with OpenShift" to log into Jaeger
-
Select a service in the drop-down (such as the
productpageservice) and click onFind Tracesto query for your service’s traces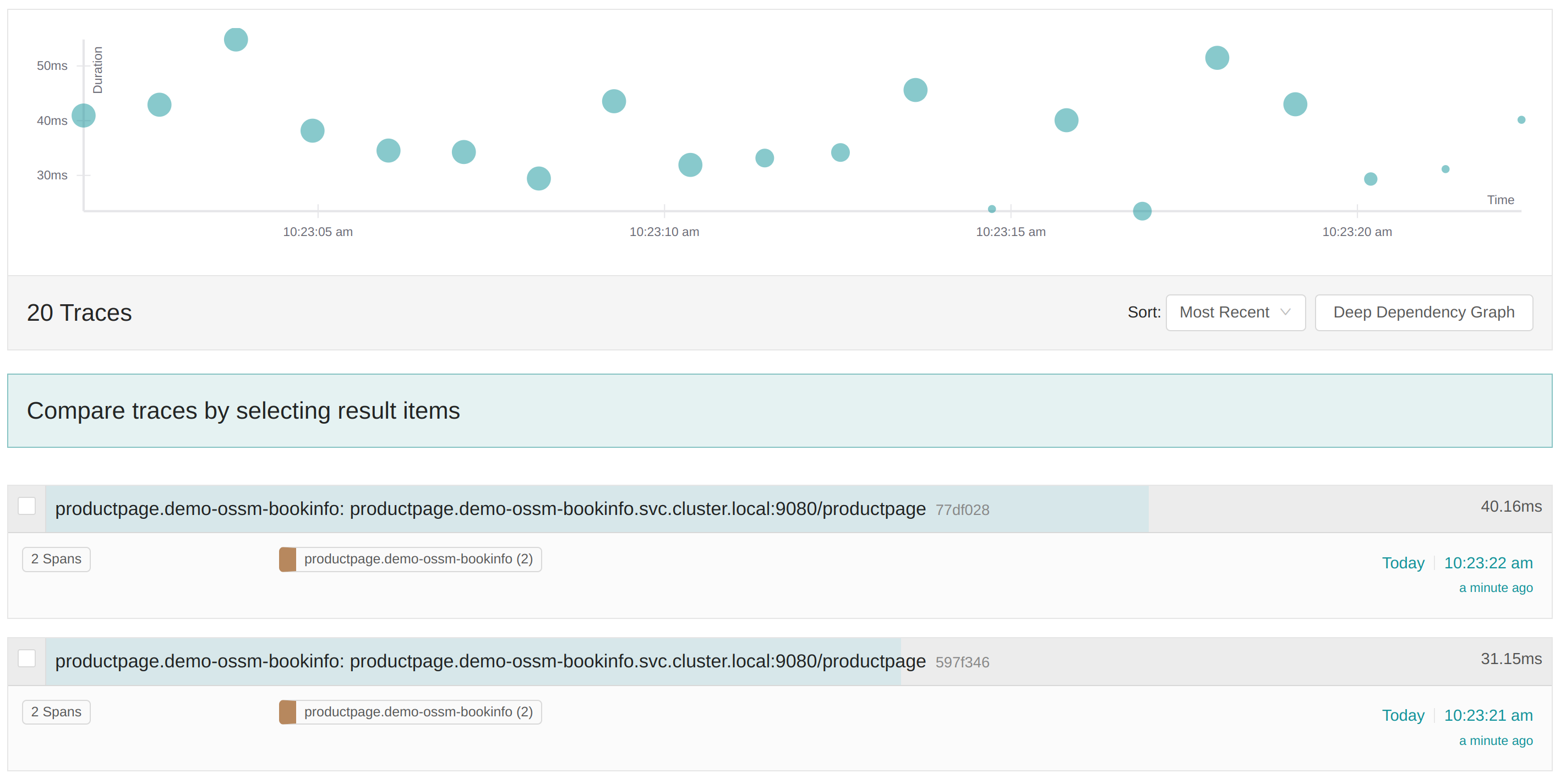
-
For more information on Jaeger and its features, see the Jaeger documentation.
-